The Future of Supercharging Healing and Performance with BPC 157
BPC 157 is one of many amazing peptides for healing catching the attention of athletes, biohackers, body builders, and those with acute and chronic injuries. BPC 157 is making its way into research protocols for healing, optimization, and regeneration. Until now, studies on BPC 157 have mostly been in rodents. Very few human studies can be found. This blog post will review the BPC 157 literature and outline potential benefits of BPC 157.
What is BPC 157?
BPC 157 is a peptide. Peptides are chains of amino acids with different sequencing. Every addition or depletion of an amino acid or a change in the sequence will change the cellular function in the cells in the body. Peptides are awesome and amazing. How do they know where to go and what to do?
BPC stands for Body Protective Compound, acquiring its name from its potent ability to quickly heal the body. BPC 157 is a small part or fragment of BPC but its benefits are profound and numerous.1
BPC 157 is a short peptide, first discovered and isolated from human gastric juice. It was initially found to help protect and heal the gut. Current studies have found its benefits go way beyond the gut, having healing potential just about anywhere in the body.
How does BPC 157 Work?
Some mechanisms of action of BPC 157 have been demonstrated, but there are more that are currently not fully understood. More studies are being conducted to uncover all ways in which BPC 157 works. Rodent studies have shown a wide variety of beneficial therapeutic effects listed below.
- One of the biggest ways BPC 157 induces healing and regeneration of cells is through a process called angiogenesis in which new blood vessels are formed. This is pivotal in regeneration as a healthy vascular network brings necessary blood flow containing healing elements to different systems in the body.2
- BPC 157 produces beneficial effects by blocking a molecule that inhibits growth and healing. By blocking this molecule, growth can continue in injured areas.1
- BPC 157 can increase growth receptors and upregulate anti-inflammatory proteins, kickstarting the healing and repair process.1
- BPC 157 stimulates cells called fibroblasts promoting collagen production, a critical structural protein for skin, connective tissue, and bones.1
- BPC 157 optimizes neurotransmitters in the brain playing a role in brain health and mood.3,4
- Lastly, BPC 157 has been found to increase nitric oxide production contributing to the migration of healing cells to an injured area by increased blood flow. More nitric oxide means more energy and oxygen to aid in healing of an injured area.1
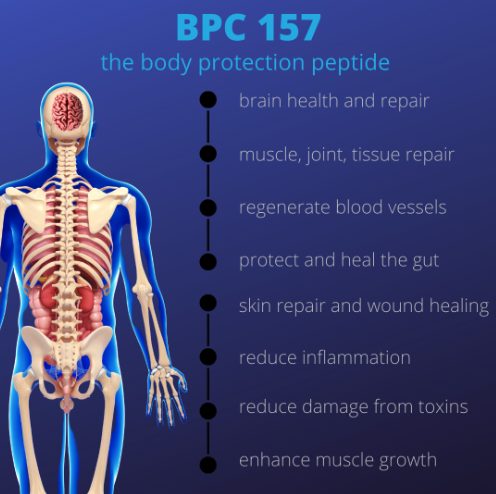
What Are the Benefits of BPC 157?
- Accelerates healing process of tendons, ligaments and bone1-3,5
- Enhances general body repair and wound healing
- Protects against formation of scar tissue6
- Protects and heals the digestive system (reflux, ulcers, Ulcerative Colitis, IBS, colitis)7-10
- Heals mitochondrial damage
- Increases growth hormone receptors3
- Prevents damage from insulin toxicity11
- Reduces inflammation in autoimmune conditions12
- Improves brain health and mood
- Reduces depression and anxiety13
- Demonstrates comparable effects to antidepressants with no side effects14
- Protects against medication dependence and withdrawal15
- Promotes repair of neurons in the brain16
- Induces healing from traumatic brain injury17
- Reduces neural damage from toxins in Parkinson’s disease and MS18,19
- Decreases the effects of neurotoxins
- Blocks long term effects and damage from corticosteroid injections20
- Balances neurotransmitter production in the brain4
- Protects the cardiovascular system21,22
- Promotes nerve healing even in traumatic nerve injury23
- Improves response to viruses and allergens24
- Counteracts damage from toxins, severe electrolyte disturbances and heart arrythmias25,26
- Improves severe chronic conditions such as CHF27
- Reduces damage from NSAIDs like ibuprofen or advil28,29
- Fights off alcohol intoxication and aids in recovery of substance abuse30,31
- Heals skin wounds, diabetic ulcers, fistulas32
Who Might Benefit from BPC 157?
BPC 157 can be especially useful for ligament, muscle, tendon and bone injuries. It also has been reported to be helpful for healing damaged skin, burns, cuts, and healing of ulcers, damaged heart muscle, the digestive system, and the brain. It seems it has capabilities to help heal the body from virtually any acute or chronic injury.
BPC 157 Safety
BPC 157 is well tolerated. No significant adverse effects have been reported from animal studies or first-hand human experiences.
Conclusion
Peptides natural to our bodies are advancing cellular medicine by offering a wide range of powerful healing benefits. BPC 157 is just one peptide that has the potential to supercharge your healing and performance with no side effects.
It has demonstrated to play a significant role in brain, heart, and gut repair, wound healing, bone, ligament and tendon injury. It has shown promise against autoimmune and chronic disease processes. It appears BPC 157 helps optimize and promote the body’s powerful, natural ability to heal itself on a cellular level.
It is exciting to be on the forefront of peptide and cellular medicine and to see how peptides will be integrated into the future of medicine.
Have an awesome day! Dr D
-
https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/japplphysiol.00945.2010?rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed&url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org
-
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51443032_Modulatory_effect_of_gastric_pentadecapeptide_BPC_157_on_angiogenesis_in_muscle_and_tendon_healing
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6271067/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27138887/
-
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00441-019-03016-8
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8275860/
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0928425799001242?via%3Dihub
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5107594/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22300085/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17713731/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20388953/
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0928425797894740
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15531385/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10791689/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10707891/
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5333585/
-
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167011509002341?via%3Dihub
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10672997/
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5333585/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20190676/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10672992/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23782145/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19903499/
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8575535/
-
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27815173
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27060013/
-
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8551987_Doxorubicine-Congestive_Heart_Failure-Increased_Big_Endothelin-1_Plasma_Concentration_Reversal_by_Amlodipine_Losartan_and_Gastric_Pentadecapeptide_BPC157_in_Rat_and_Mouse
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22950504/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9403784/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17186181/
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20388962/
-
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.627533/full
